MRI Technology Advancement
Introducing the newest, most advanced MRI in the suburban area.
Dramatically Higher Clarity
Wider Openings for Comfort
Faster Scans for Comfort
Easy Physician Access
When It Comes To Your Health
We See The Whole Picture
A Higher Standard of Care
About Fox Valley Imaging
Comprehensive Medical Imaging
Fox Valley Imaging, conveniently located in Naperville, Illinois, off of Route 59. We provide reliable, empathetic, affordable and ethical medical imaging services. Call us and we will be happy to answer any questions you may have. We can usually accommodate urgent or same day needs.
Independent Imaging Centers Support the Patient’s Right to Choose Their Providers, Finding Higher Quality Healthcare at a More Competitive Price.
Services
What We Offer
At Fox Valley Imaging, our modern facility features cutting-edge imaging machines and trained, experienced technicians who will help to make your experience fast and comfortable. They are there to answer any questions you may have as well as to operate the imaging machines to provide the best services possible for you and your physician. Our services include:
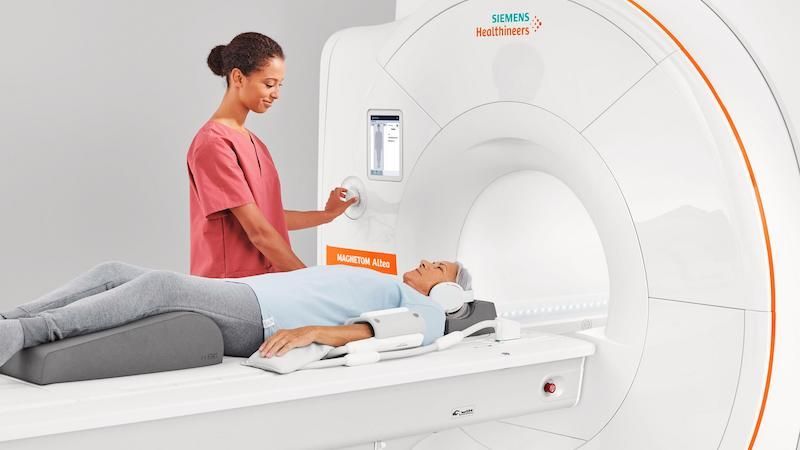
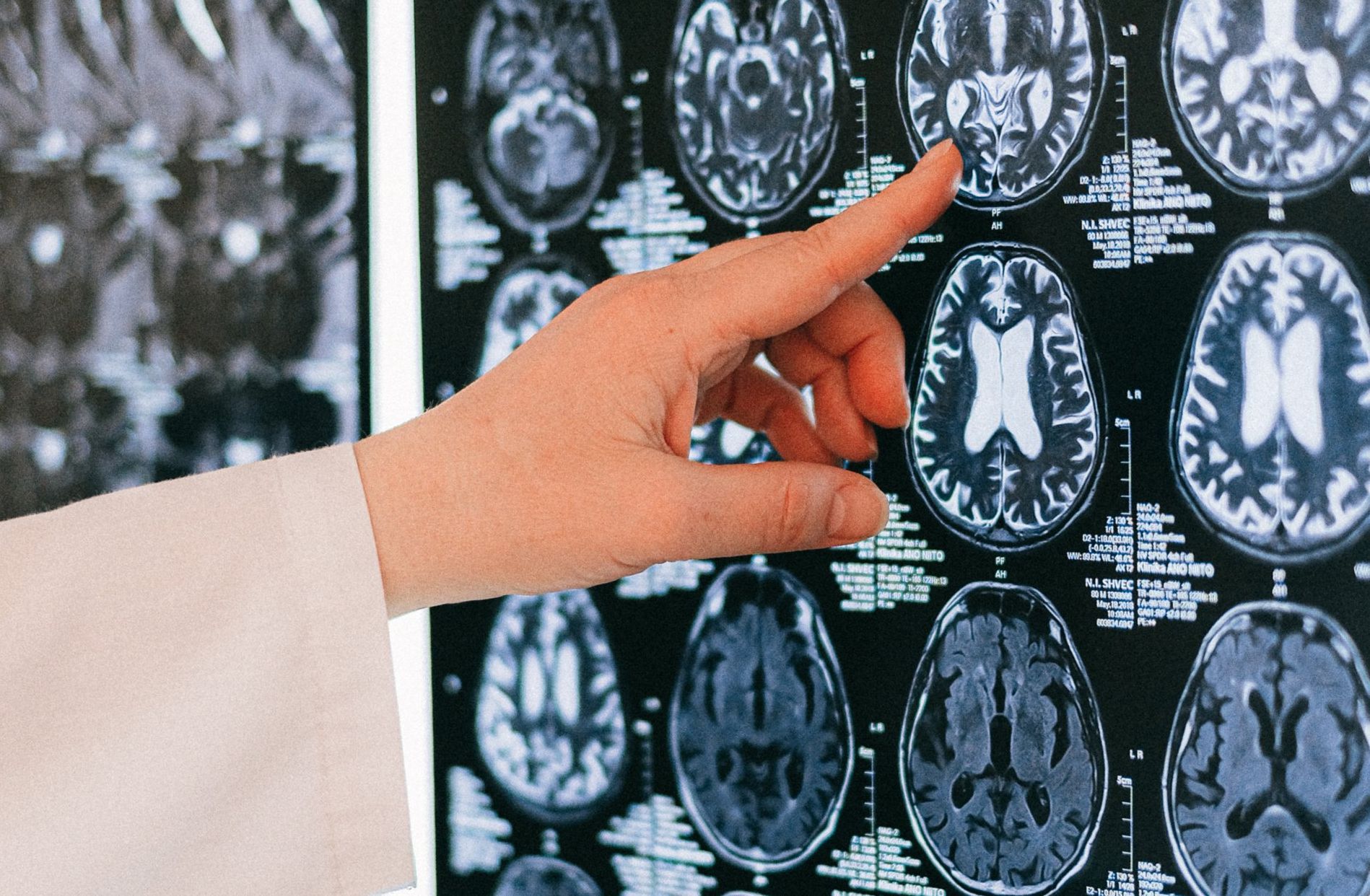
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize internal structures of the body in detail. MRI makes use of the property of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to image nuclei of atoms inside the body.
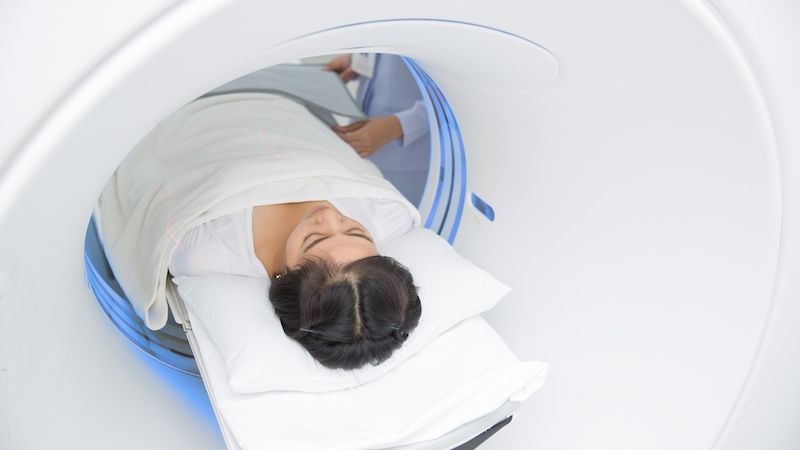
CT (Computed Tomography)
X-ray computed tomography, also computed tomography (CT scan) or computed axial tomography(CAT scan), is a medical imaging procedure that utilizes computer-processed X-rays to produce tomographic images or ‘slices’ of specific areas of the body. These cross-sectional images are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in various medical disciplines.
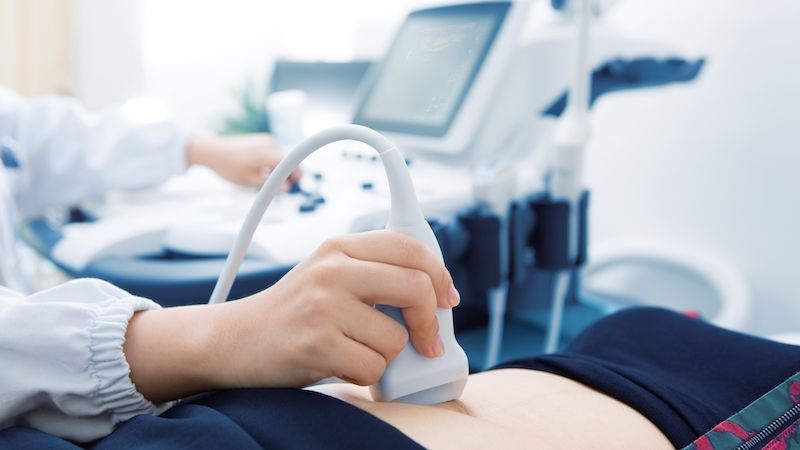
Ultrasound
Diagnostic sonography (ultrasonography) is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique used for visualizing subcutaneous body structures including tendons, muscles, joints, vessels and internal organs for possible pathology or lesions.
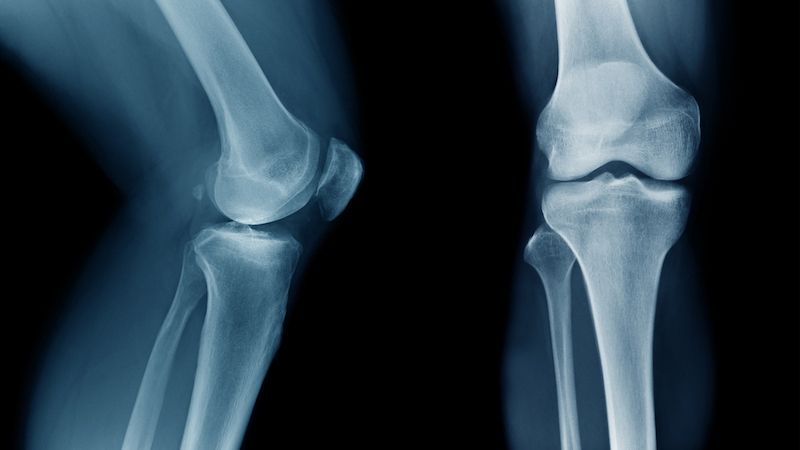
Digital X-Rays
Digital radiography is a form of X-ray imaging, where digital X-ray sensors are used instead of traditional photographic film. Advantages include time efficiency through bypassing chemical processing and the ability to digitally transfer and enhance images.

Bone Density Scanning
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD). Two X-ray beams with different energy levels are aimed at the patient’s bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted out, the BMD can be determined from the absorption of each beam by bone. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry is the most widely used and most thoroughly studied bone density measurement technology.

Echocardiography
Echocardiogram, often referred to cardiac echo or simply an echo is a sonogram of the heart. (It is not abbreviated as ECG, which in medicine usually refers to an electrocardiogram.) Echocardiography uses standard two-dimensional, three-dimensional, and Doppler ultrasound to create images of the heart.
Advantages
Our Deep Core Values Sustain Our Business and Set Us Apart
We Care For You
For over 30 years we have strived to see each patient as a member of the family. You will notice the difference in the time we take to make sure we have the best images, your comfort, and the friendliness of our staff.
Quality First
We have been the local forerunners in image quality with the use of newer advanced systems which provide greater clarity. Greater clarity provides a more precise diagnosis.
Doctors love the detail in our images!
Lower Cost
Hospitals take advantage of their captive audience with very inflated imaging costs. Independent imaging facilities offer choice, more personal control, and lower costs.
With today’s high deductible insurance plans, we can help you save significant out-of-pocket costs.
Benefits
Better Service Guaranteed
Insurance Plans
Most insurances are accepted. Scheduling will work through the details with you.
Easy Parking
Park at the door. Fast, free, and convenient parking.
Fast Scheduling
Fast scheduling, even Same-day can often be accommodated when required.
We’re here to hear your concerns
At Fox Valley Imaging, we’ve been providing professional imaging services for our patients for over 21 years.
Have questions?
Schedule an Appointment!
Just tell us when you prefer to come to our facility and we’ll get right back to you with some options.
Contact Us
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
How are MRIs different from X-rays?
MRI is so precise, the image taken is often the same as looking directly at the tissue (only in black and white). This clarity can lead to the early detection of disease and helps reduce the number of some diagnostic surgeries. Early detection is very valuable since it can lead to early treatment. Unlike X-rays, there are no known side effects to MRI.a computer can construct an image on a monitor which can be recorded on film or magnetic tape for future reference.
For what types of medical problems is MRI the most useful?
MRI is best at seeing soft tissue. Therefore, it is very useful for brain and nervous disorders (stroke, traumatic injuries, fluid in the skull, tumors, multiple sclerosis, and spinal conditions or diseases). It is also beneficial for musculoskeletal problems (ligament, tendon and cartilage injuries) and subtle bone injuries and tumors. Newer applications include imaging of the abdominal and pelvic organs (liver, kidneys, pancreas, uterus and ovaries). MR can also evaluate the heart and blood vessels.
How does MRI work?
The body is made up tiny particles called atoms. Protons located inside the atoms continually spin at random. The magnetic field from the MRIs magnet makes the protons line up together and spin in the same direction. Then, a radio frequency signal is beamed into the magnetic field. This signal disrupts the protons, causing them to spin out of alignment. By then turning the signal off, the protons return to their aligned position and release energy.

